Blockchain for Beginners – Explanation, History, and Real Examples
Blockchain – a term that shows up a lot when discussing cryptocurrency. But do any of us actually understand what blockchain is, how it works, or even know how it looks like?
This article aims to explain what blockchain really is in as beginner-friendly manner as possible, while at the same time providing actual examples of how this technology looks like and how it works.
So if you’re curious as to what the blockchain technology is and want to finally get a simple yet understandable explanation of blockchain for beginners, look no further!
But first, let’s take a look at a few blockchain facts and characteristics…
Blockchain Facts and Characteristics
- Many people think that it is Bitcoin that makes the blockchain technology so widely-used, but it’s simply not true. Blockchain has a much bigger usage than just cryptocurrency. Bitcoin just happens to also use it.
- There are many different types of blockchain.
- Blockchain technology works in a decentralized way, meaning there’s no need for a third party integration. Everyone can access blockchain the same way.
- Each and every transaction registered on the blockchain technology is cryptographically encrypted.
When Was Blockchain Invented?
The early beginnings of a blockchain-like protocol took place in 1982 when David Chaum, a cryptographer, issued his thesis – “Computer Systems Established, Maintained, and Trusted by Mutually Suspicious Groups.”
Then further work by different people had been performed throughout the years, all in hopes to create a cryptographically encrypted chain of blocks that registers data with unalterable time stamps.
The design was slowly coming together, especially when in 1992 Haber, Stornetta, and Dave Bayer added hash trees into its structure. This allowed one block to hold more than one document and included the hash – previous block’s summary.
Three years later, the New York Times started publishing their work on a weekly basis, which may have provided inspiration to other creators and cryptographers.
The blockchain we know today – mostly thanks to its usage within cryptocurrency – has first been conceptualized in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto (a person or a group of people that stay anonymous till today).
What Satoshi Nakamoto did differently is think of a way to timestamp each block without the need for a third-party integration, allowing blockchain to operate within a peer-to-peer system.
But What Really Is Blockchain? Blockchain Definition for Beginners
Blockchain is a technology of distributed ledgers that allows for storing and checking information included in it. It’s basically cryptographically connected records of data that once recorded cannot be edited or cancelled in any way.
This technology is known for its ability to maintain the security of the data stored and the fact that it works on a decentralized, peer-to-peer system.
Now, while researching other articles written on this topic, we found that their authors stop with this definition of blockchain, not really explaining it further.
But it may be difficult for non-tech-savvies or simply beginner traders to actually understand what these complicated sentences mean in practice.
So, what does it mean that the blockchain technology is a network of distributed ledgers? Does it look the way it’s usually presented?
Well…not exactly.
How Does Blockchain Look Like? A Real Example of Blockchain
To get a better understanding of what blockchain is, we have to see its true form. So, before we go any further explaining the blocks, the name, the data stored, and uses of blockchain, let’s see a real example of this technology.
And no, it’s not the blocks everyone’s presenting.
Here’s an actual example of how data stored in blockchain may look like
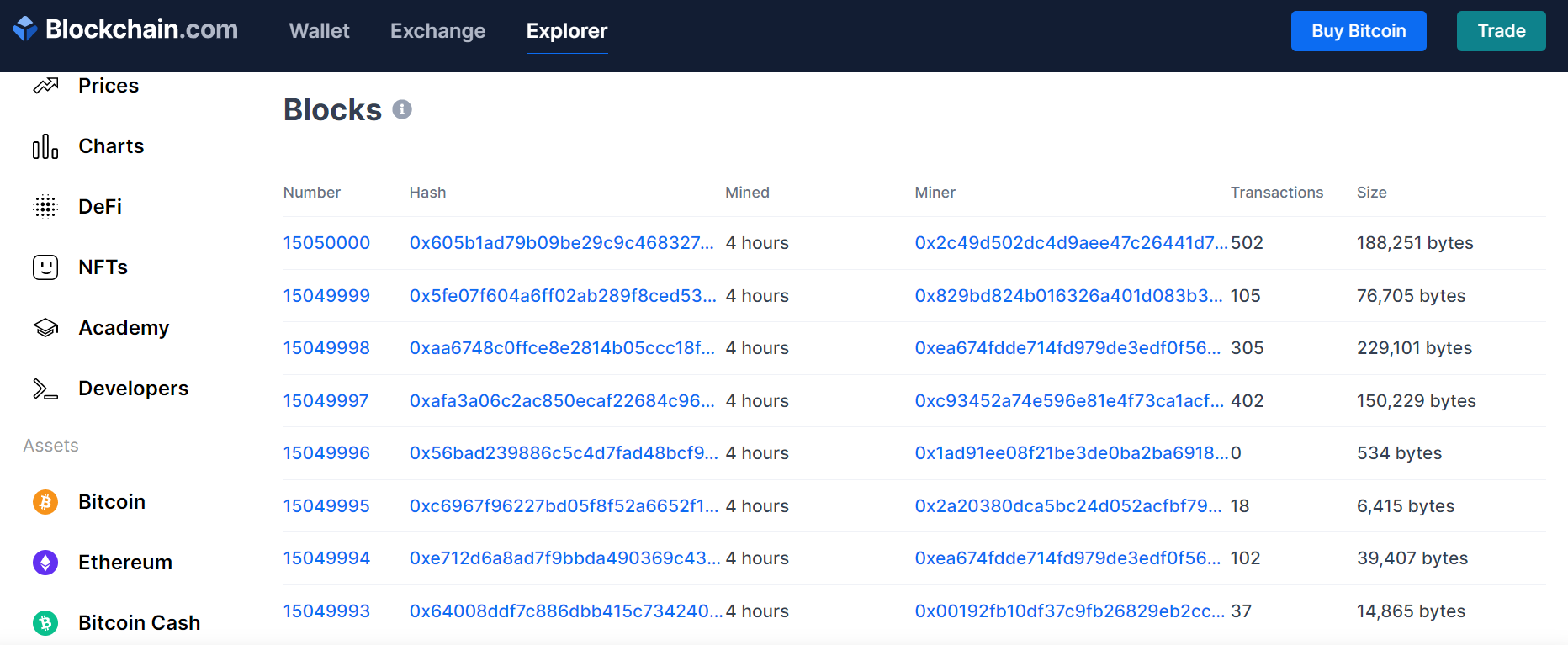
Basically, a sequence of numbers and letters. Not as interesting, we know. But that’s how blockchain looks like.
And now that we have the real example presented and we know what blockchain actually is – a string of numbers and letters, let’s dive into a more beginner-friendly explanation of the blockchain elements and the way it operates.
Blockchain Elements – What Comprises Blockchain?
Let’s now focus on what those sequences of numbers and letters actually hide. We’ll go through the elements of blockchain in an illustrative way to help visualize the whole thing.
We already know that the blockchain technology registers and keeps data, just like ledgers do.
But to actually visualize how blockchain works, it’s best to present it in the form of a chain. So – think of an actual chain and the chain links it has that are all connected together forming one structure.
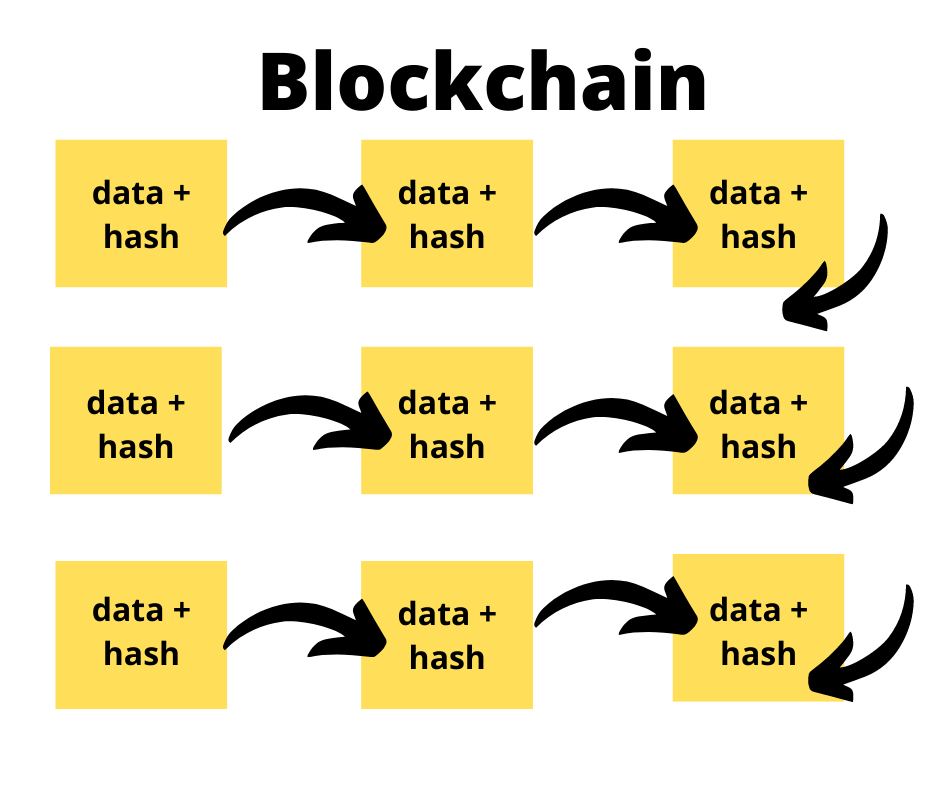
Blockchain as its name suggests is a set of blocks that are connected together and form a kind of chain. Each blockchain’s block has a limited amount of data that can be registered on it and once that limit is reached, the block is complete and a new one is created.
Now, each blockchain block comprises the information registered on it and hash.
Hash is a mathematical code that provides a summary of the block it’s connected to and because of the hash that’s registered in each block, the whole blockchain is directly connected.
So at its core, blockchain is simply:
What Does it Mean that Blockchain Is Decentralized and Distributed?
Let’s go back to what we said at the beginning of this article – “blockchain is a technology of distributed ledgers”.
Because blockchain operates in a decentralized system, it means that there’s no controlling party, entity, or individual standing at the top of blockchain, making the decisions, pulling the strings, or having access to specific data.
Instead, all users have the same access to the data registered on the blockchain technology. There is no risk than one, controlling party will gain access to more than half of the data stored on blockchain to manipulate it and there is also little to no risk that anyone will be able to hack blockchain since there’s no central data storing centre.
How Is Blockchain Safe from the Changes to the Registered Data?
Even though the ledgers are distributed, each block contains the data registered on it AND the summary of the previous block – hash. Now, because of such connections we can be sure that the data kept within blockchain was not altered with.
Why?
Because if you edit one piece of data in a block, its hash would have to change, affecting the next block, and the next one, and then the next one.
It would also mean that all users supporting the blockchain’s network (blockchain miners) would have to accept the changes made in the edited block. If they don’t do that, the changes are dismissed.
Fun fact: if there comes a situation where 30% of blockchain miners are in favour of the changes, but the other 70% is not, we’re met with a situation called the network’s FORK, which simply put is when blockchain splits into two chains. But that’s a topic for later! Let’s go back to blockchain’s basics now.
Blockchain miners are people who share the computing power of their computers, graphic cards etc. to solve complicated mathematical problems to support the network, secure it, and approve transactions.
Once one mathematical problem is solved, the miner who shared their computer or other device for that purpose, receives a reward, e.g., for Bitcoin Blockchain miners it’s a small part of BTC.
Let’s now drift away from cryptocurrency and show a few examples of other industries in which blockchain is used.
Examples of Industries That Use Blockchain
Because of Bitcoin’s popularity, many people believe cryptocurrency is the only space for blockchain usage.
But the blockchain technology is extremely well-thought-out and what’s the most important – it allows for registering data in a cryptographically encrypted way, so how could it be only used in one field?
Many industries take advantage of the blockchain technology, including those working in finance, medical professionals, precious metal industry workers, art work specialists, real estate workers, and many many more.
Some industries use it for medical data storage, others for transparent transaction registering, identity protection, smart contracts, and more.
The examples of blockchain uses are truly endless, which just goes to prove its efficiency and usefulness.
Wait, so it’s actually that simple?
We want to point out that this article aims at beginners trying to understand the essence of what blockchain is.
The whole technology is pretty complicated, involving advanced mathematical, computer, technology, IT, and cryptographic terms and problems.
Only people truly mathematically or other close field’s gifted will be able to fully understand what blockchain really is and dive into its complicated nature.
But, for the purpose of using cryptocurrency, it’s worth knowing the simplified way as to how blockchain operates and the way it’s used.